A Comprehensive Guide to Preform Types and Manufacturing Characteristics of Preform Molds
Preforms are semi-finished products used in blow molding to create plastic bottles and containers. Understanding the types of preforms and the manufacturing nuances of preform molds is critical for industries like packaging, beverages, and cosmetics. This article explores the common types of preforms and the key manufacturing characteristics of preform molds, optimized for SEO with keywords such as preform types, preform mold manufacturing, PET preforms, blow molding, and injection molding.
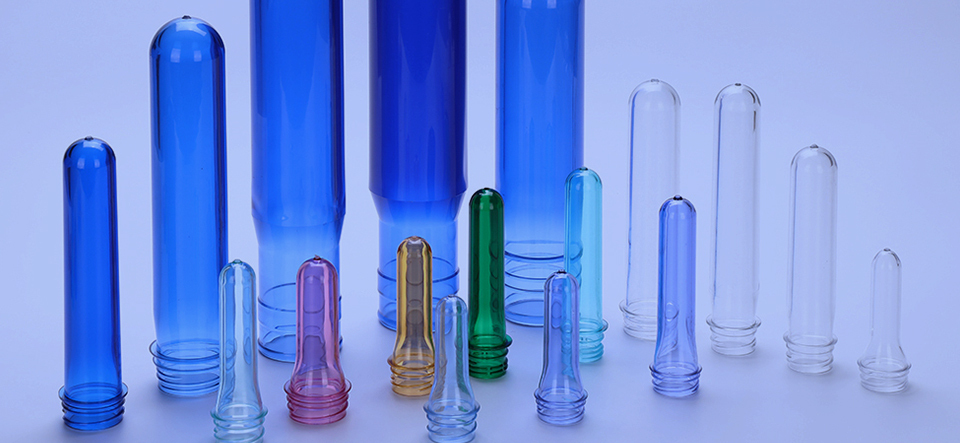
1. Types of Preforms
Preforms are classified based on material, design, and application. Here are the most common types:
1.1 PET Preforms
Description: Made from polyethylene terephthalate (PET), these preforms are lightweight, recyclable, and widely used for beverage bottles.
Applications: Water, soda, juice, and edible oil packaging.
Keywords: PET preforms, recyclable plastic preforms, beverage bottle preforms.
1.2 PP Preforms
Description: Polypropylene (PP) preforms offer high chemical resistance and are suitable for hot-fill applications.
Applications: Pharmaceutical bottles, syrup containers, and hot-fill food packaging.
Keywords: PP preforms, polypropylene preforms, hot-fill preforms.
1.3 HDPE Preforms
Description: High-density polyethylene (HDPE) preforms are durable and resistant to impacts, making them ideal for household chemicals and cosmetics.
Applications: Detergent bottles, shampoo containers, and cosmetic packaging.
Keywords: HDPE preforms, durable preforms, cosmetic bottle preforms.
1.4 Customized Preforms
Description: Preforms can be tailored in terms of neck finish, wall thickness, and color to meet specific branding or functional requirements.
Applications: Specialty packaging for premium products.
Keywords: Custom preforms, tailored preforms, specialty bottle preforms.
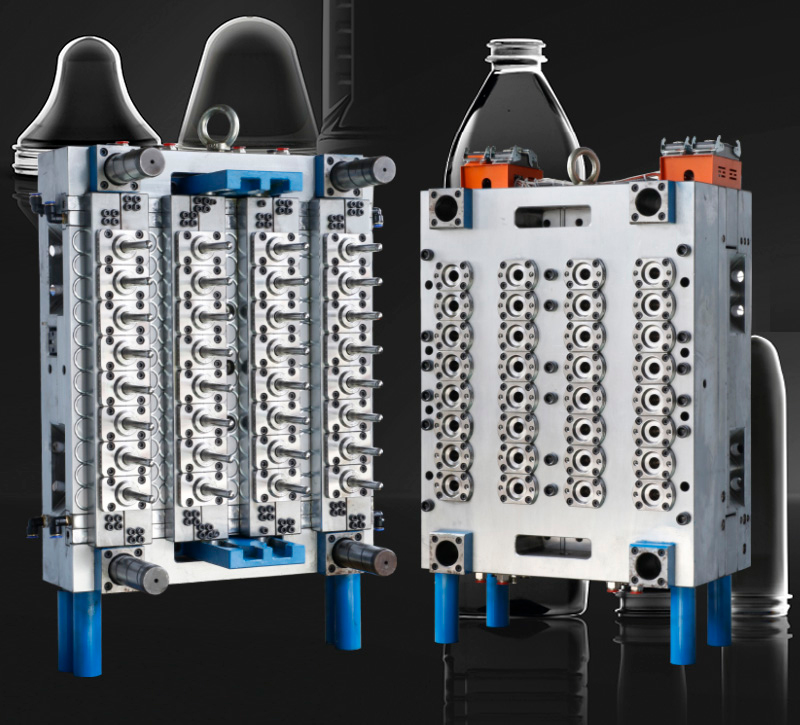
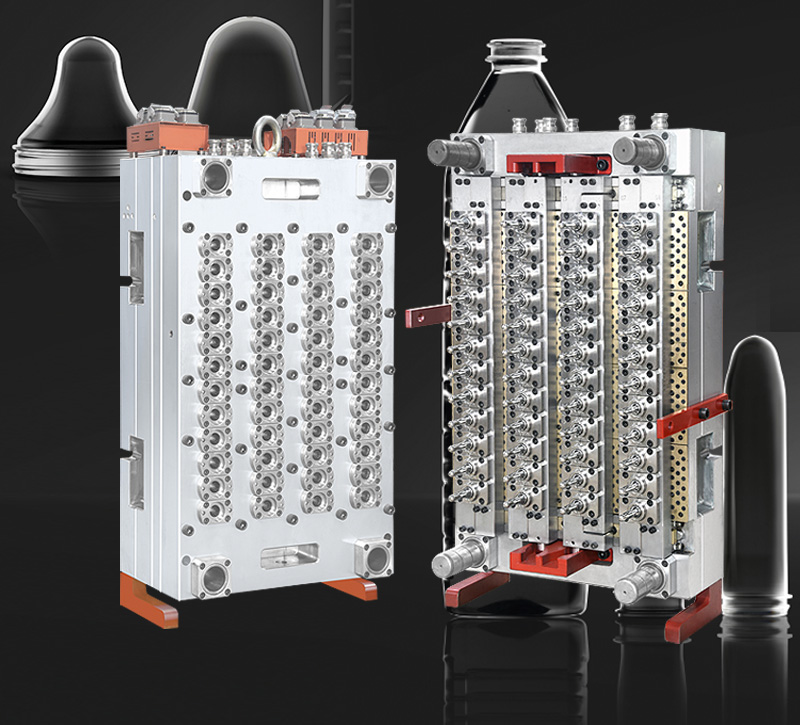
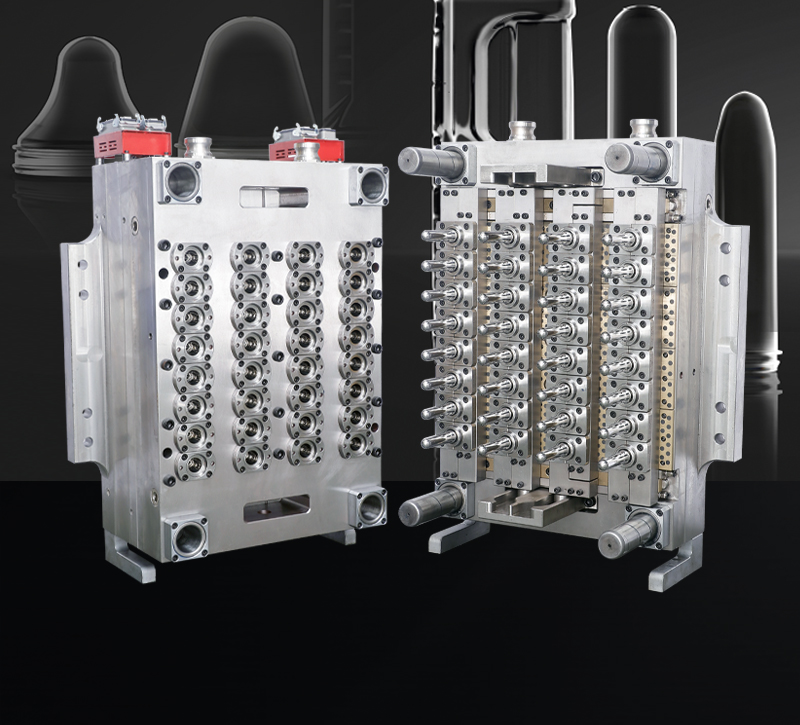
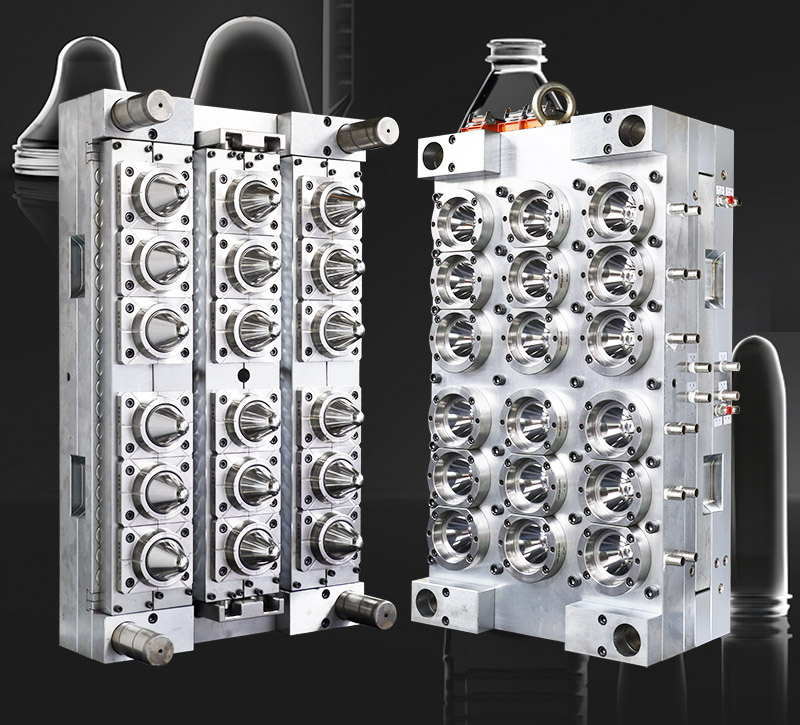
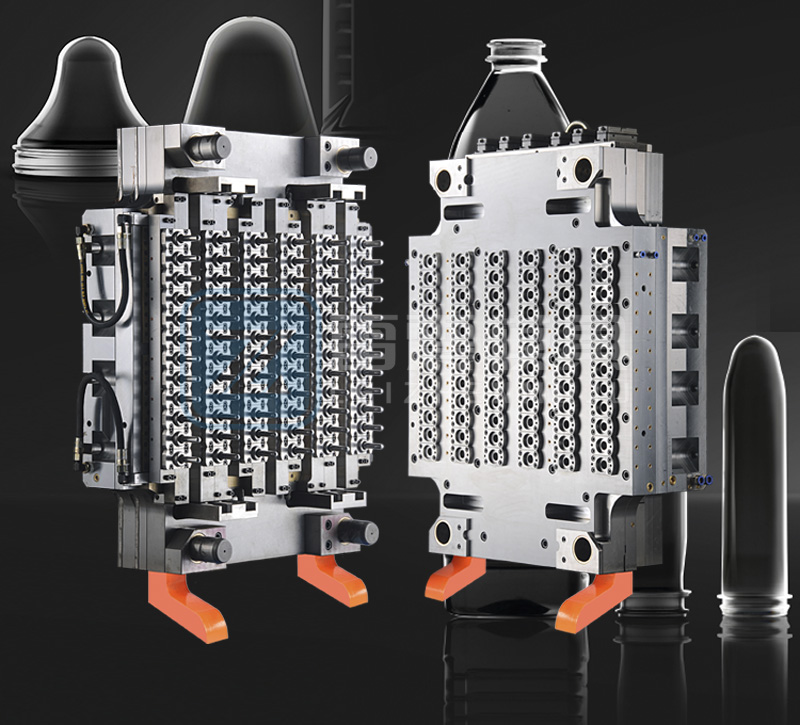
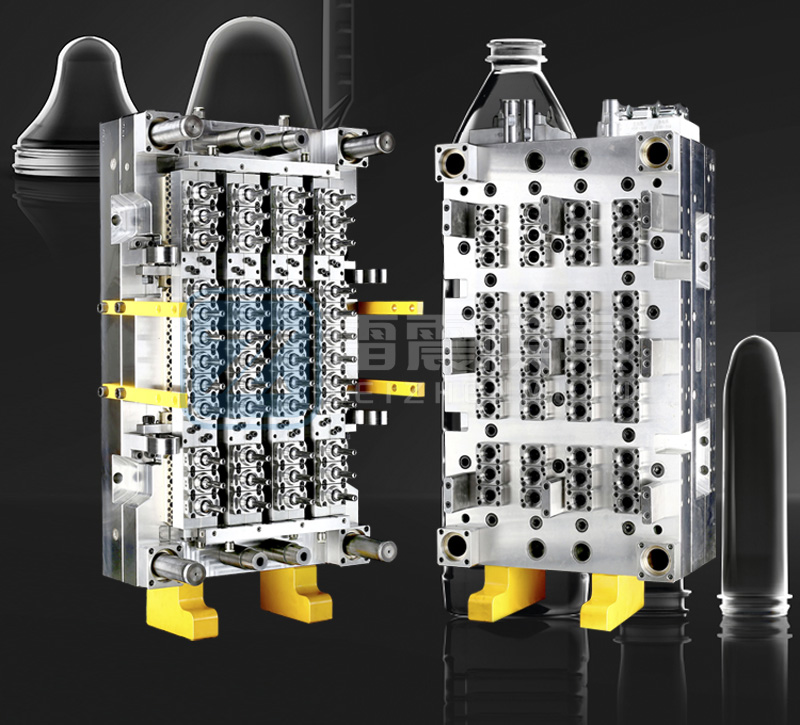
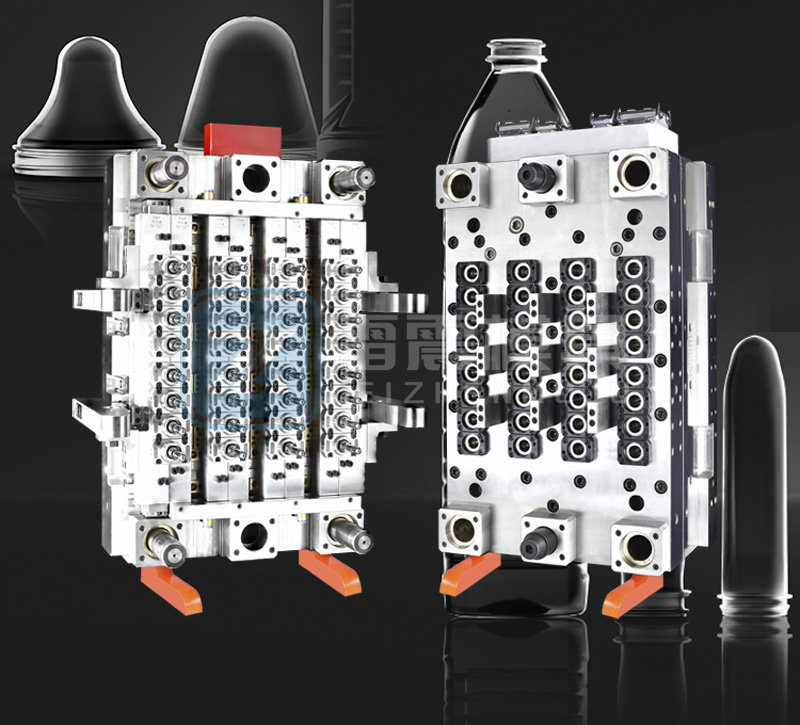
2. Manufacturing Characteristics of Preform Molds
Preform molds are critical for producing high-quality preforms. Their manufacturing involves precision engineering and attention to detail.
2.1 High-Precision Machining
Description: Preform molds require CNC machining and EDM (electrical discharge machining) to achieve tight tolerances and smooth surface finishes.
Importance: Ensures consistency in preform dimensions and wall thickness.
Keywords: Precision mold manufacturing, CNC machining for molds, EDM for preform molds.
2.2 Cooling System Design
Description: Efficient cooling channels are integrated into the mold to ensure uniform cooling and reduce cycle times during injection molding.
Importance: Prevents defects like warping or crystallinity issues in preforms.
Keywords: Mold cooling system, injection molding efficiency, preform quality control.
2.3 Material Selection
Description: Preform molds are typically made from high-grade stainless steel (e.g., 420SS, H13) to withstand high pressure and temperature cycles.
Importance: Enhances mold durability and longevity.
Keywords: Stainless steel molds, mold durability, preform mold materials.
2.4 Multi-Cavity Design
Description: Molds often feature multiple cavities to maximize production output while maintaining consistency across preforms.
Importance: Improves production efficiency for high-volume orders.
Keywords: Multi-cavity molds, high-output preform molds, production efficiency.
2.5 Surface Treatment
Description: Molds undergo polishing, coating (e.g., chromium plating), or nitriding to enhance wear resistance and facilitate easy release of preforms.
Importance: Reduces maintenance needs and extends mold life.
Keywords: Mold surface treatment, polished molds, preform mold maintenance.
Conclusion
Preforms and their molds play a vital role in the packaging industry. Understanding the types of preforms (e.g., PET, PP, HDPE) and the manufacturing specifics of preform molds (e.g., precision machining, cooling design, material selection) is essential for optimizing production quality and efficiency. By leveraging advanced mold manufacturing techniques, businesses can meet diverse packaging demands while ensuring sustainability and cost-effectiveness.