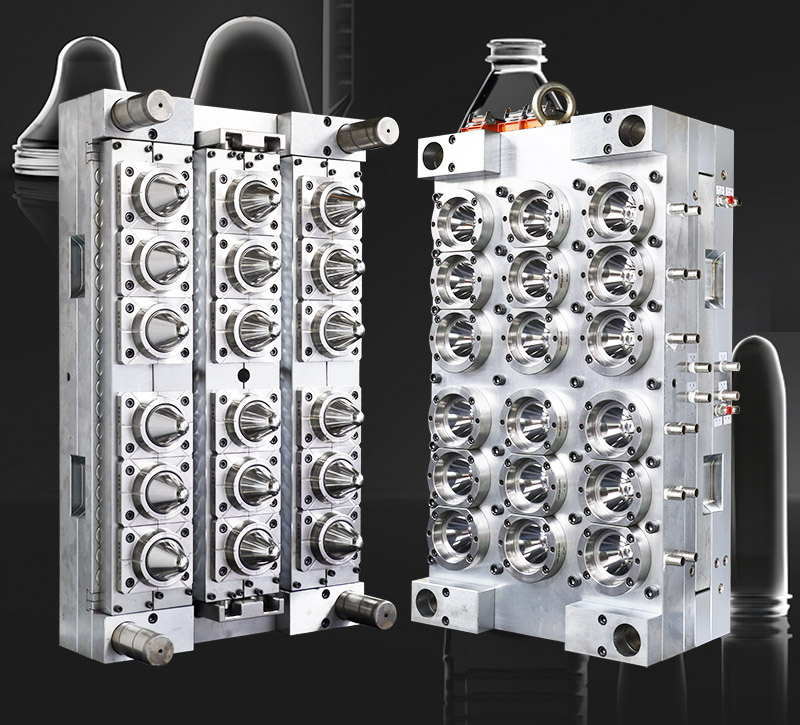
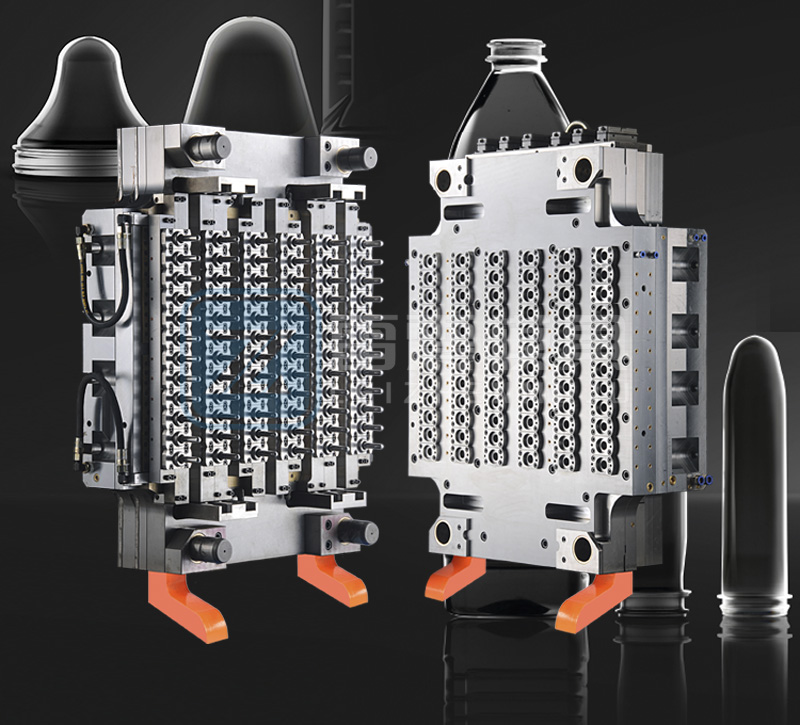
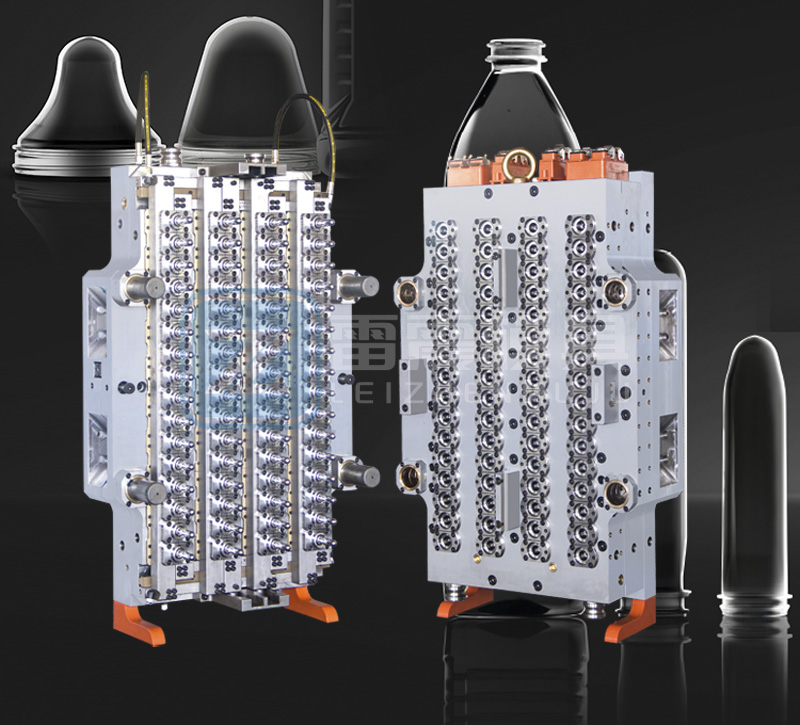
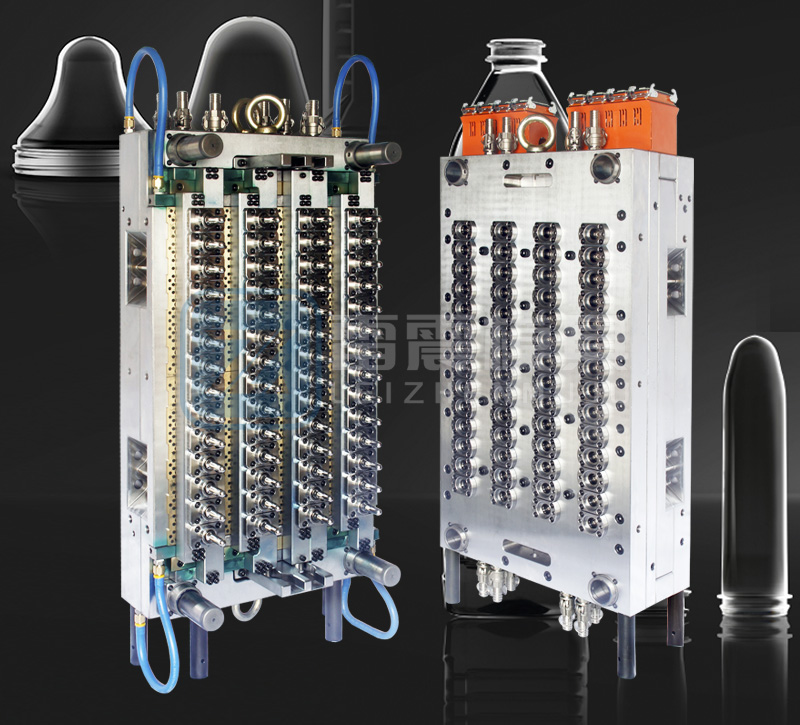
Complete Guide to PET Preform Mold Manufacturing, Maintenance & Production
Key Considerations in PET Preform Mold Manufacturing
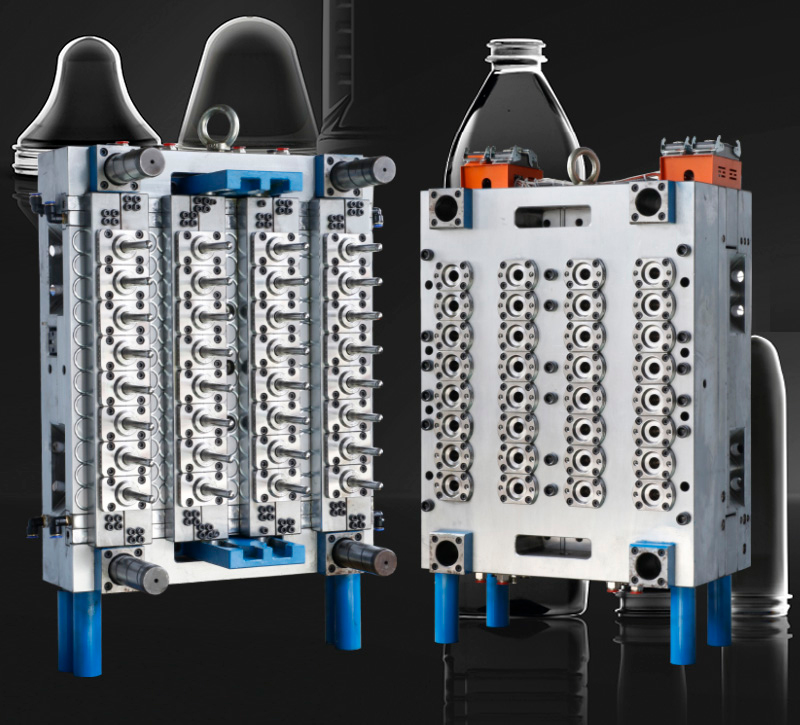
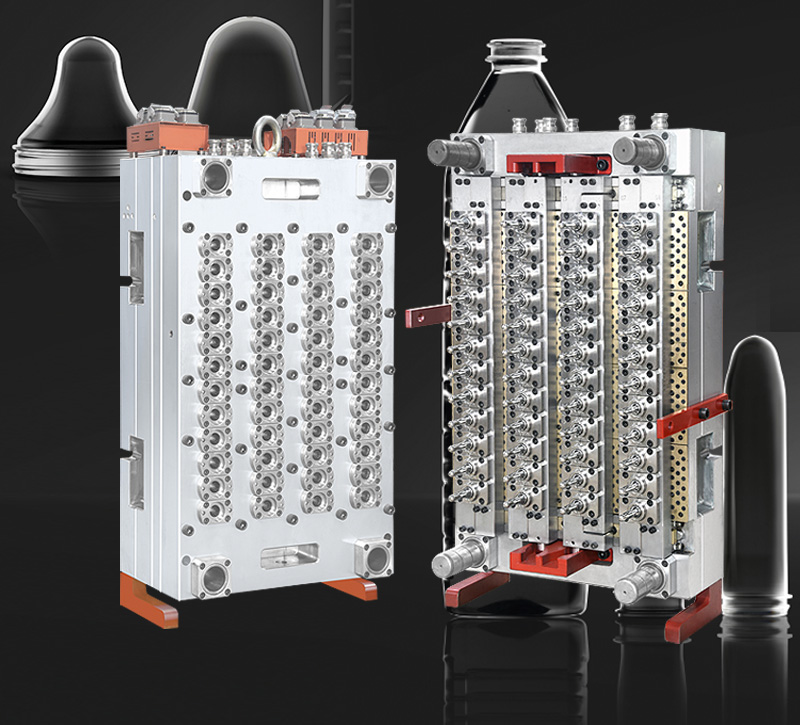
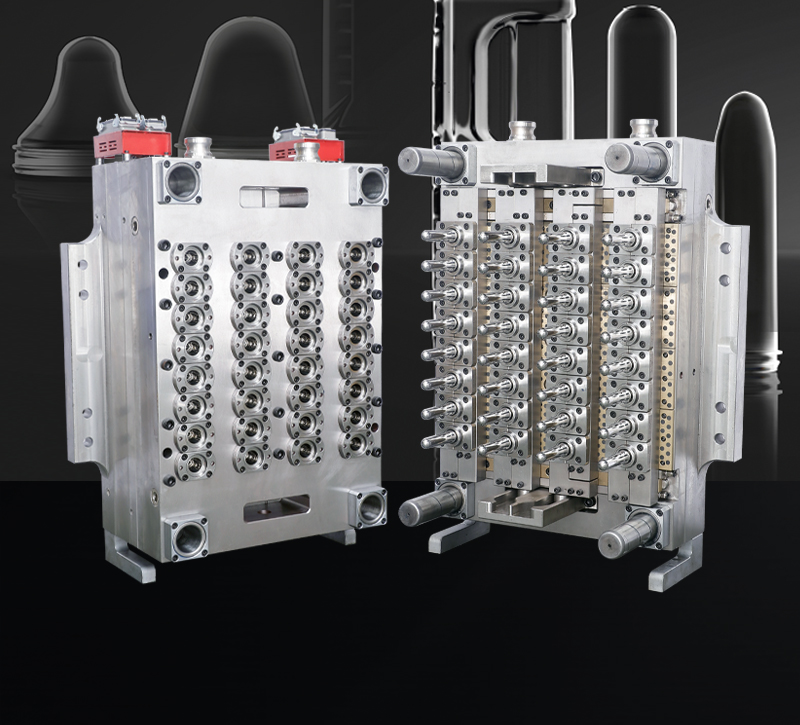
Manufacturing high-quality PET preform molds requires precision engineering and meticulous attention to detail. Here are the critical aspects to consider:
Material Selection
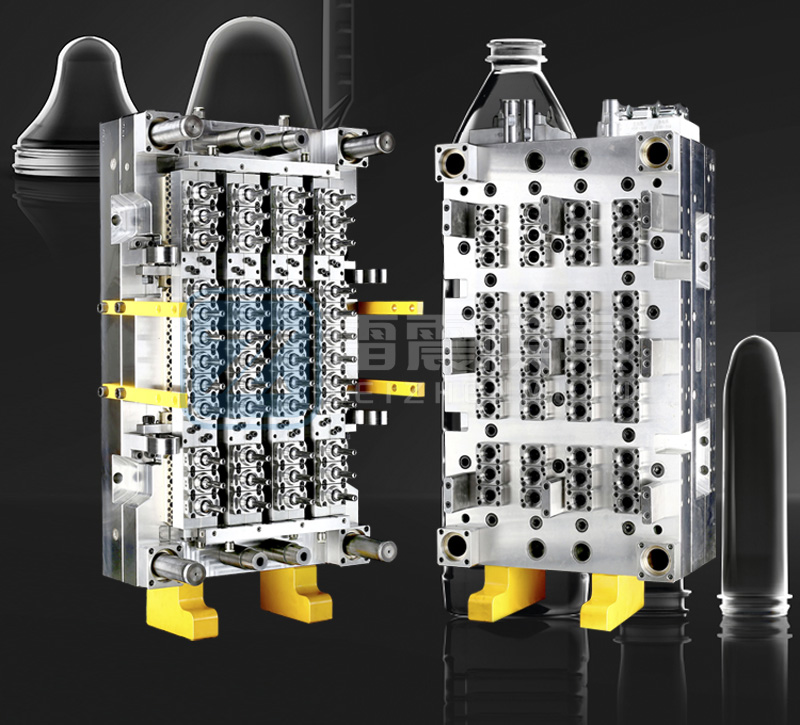
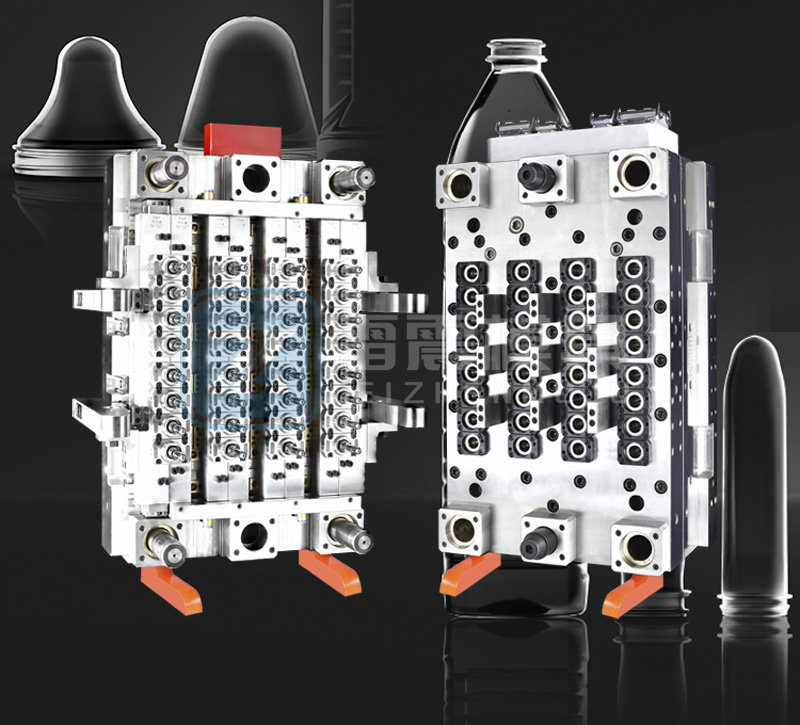
Use premium mold steels such as H13, S136, or 420 stainless steel for superior corrosion resistance and durability. Critical components like injection nozzles and gate inserts should utilize hardened steels or carbide materials to withstand abrasive PET materials.
Cooling System Design
An efficient cooling system is paramount for consistent preform quality. Implement conformal cooling channels that follow the contour of the cavity to ensure uniform temperature distribution. Proper cooling reduces cycle time by up to 30% and minimizes residual stresses in preforms.
Venting Design
Adequate venting prevents gas traps and burn marks. Vent depths should be carefully calculated (typically 0.015-0.02mm for PET) and placed strategically along parting lines and ejector pins.
Surface Finish
Cavity surfaces require high-polish finishes (typically SPI A1 or better) to ensure easy ejection and excellent preform surface quality. Textured surfaces should be avoided in the main body to prevent sticking.
Dimensional Accuracy
Maintain tight tolerances (±0.005mm) for critical dimensions like neck finishes and gate areas. Implement proper shrinkage compensation (PET typically shrinks 1.5-2.0%) in mold design.
Gate Design
Hot runner systems with needle-valve gates provide precise control over injection. Gate geometry must be optimized to prevent visual defects and ensure proper sealing.
Essential Mold Maintenance Procedures
Daily Maintenance
Clean mold surfaces with specialized mold cleaners before and after production runs
Lubricate moving components with high-temperature mold lubricants
Inspect for wear on guide pins, bushings, and ejector systems
Verify proper function of thermal control systems
Weekly Maintenance
Disassemble and thoroughly clean venting channels
Inspect and polish any minor surface imperfections
Check hot runner system for proper heating and electrical continuity
Verify cooling channel flow rates and temperatures
Monthly Maintenance
Complete disassembly for deep cleaning and inspection
Measure critical dimensions against original specifications
Replace worn components (ejector pins, seals, heaters)
Re-calibrate temperature controllers and sensors
Seasonal/Annual Maintenance
Perform non-destructive testing for stress cracks
Re-polish cavity surfaces if needed
Upgrade obsolete components
Update maintenance documentation
Producing High-Quality PET Preforms: Process Parameters
Material Preparation
Dry PET resin properly to moisture content below 50 ppm. Use dehumidifying dryers with -40°C dew point for 4-6 hours at 150-160°C.
Injection Molding Parameters
Temperature Settings:
Barrel zones: 260-285°C (gradual increase toward nozzle)
Nozzle temperature: 280-285°C
Mold temperature: 8-12°C (cavity), 8-15°C (core)
Hot runner: 285-295°C
Injection Parameters:
Injection speed: High initial speed (90-95% of maximum)
Switchover point: 95-98% of cavity filled (switch to packing phase)
Holding pressure: 40-60% of injection pressure
Cooling time: 8-12 seconds (depending on wall thickness)
Critical Quality Control Points
Visual Inspection: Check for bubbles, black spots, cloudiness, or gate defects
Dimensional Verification: Measure neck finish dimensions, overall length, and wall thickness distribution
Weight Control: Maintain consistent preform weight within ±0.1g tolerance
Intrinsic Viscosity (IV): Monitor IV drop to ensure proper molecular weight
Crystallinity: Ensure amorphous structure (typically <5% crystallinity)
Troubleshooting Common Defects
Stretching Lines: Increase mold temperature, optimize injection speed
Cloudiness: Improve drying, check for contamination
Gate Defects: Adjust gate temperature, optimize holding pressure
Short Shots: Increase injection pressure, check venting
Yellowing: Reduce barrel temperatures, check thermal degradation